Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of the global economy, driving innovation, creating jobs, and fueling growth. However, as these businesses mature, they often face significant challenges securing the capital needed to scale. One powerful solution is an Initial Public Offering (IPO). This guide is designed to help SMEs navigate the complexities of the IPO process, equipping entrepreneurs with the knowledge to make informed decisions about going public and leveraging the market to fuel their growth ambitions.
Understanding SME IPOs
What is an SME IPO?

An SME IPO involves a small or medium-sized business offering shares to the public for the first time. This process allows companies to raise capital from public investors, list their shares on a stock exchange, and gain access to a broader pool of capital. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- Share Offering: The company sells shares to the public for the first time, generating significant capital.
- Pricing Strategy: Shares are priced to meet fundraising goals while balancing investor expectations.
- Stock Exchange Listing: Shares are listed on a stock exchange, providing liquidity and access to public markets.
- Compliance Requirements: As a public company, it is required to have increased obligations in terms of reporting, governance, and transparency.
Typically, SMEs raising between $10 million and $100 million through an IPO benefit from enhanced visibility, capital for growth, and increased market credibility.
Key Benefits of an SME IPO
Accelerating Growth

An IPO can accelerate business expansion by providing the capital for scaling operations. This influx of funds can be used for:
- Expansion Projects: Investing in new markets, facilities, or product lines.
- Research and Development: Enhancing product offerings and innovation.
- Acquisitions: Acquiring complementary businesses to fuel growth.
Equity Infusion
Going public allows SMEs to raise equity without incurring high-interest debt, strengthening their balance sheet and financial stability.
Investor Exit

An IPO offers an exit strategy for early investors, such as founders, family offices, or venture capitalists, allowing them to realise investment returns.
Enhanced Visibility and Recruitment
Being publicly traded raises the company’s profile, enhances credibility, and attracts top talent through stock compensation and options.
Acquisition Currency

Publicly traded stock provides a valuable currency for mergers and acquisitions, facilitating strategic growth.
Drawbacks of Pursuing an SME IPO
Dilution of Control
Owners may experience reduced control over the company due to the dilution of their equity stakes.
Increased Reporting Burdens

Public companies face higher regulatory and compliance costs, including detailed financial reporting and governance requirements.
Pressure to Meet Expectations
Publicly listed companies are constantly scrutinised to meet financial forecasts and investor expectations, which can be stressful for management.
High Initial Costs
The costs associated with an IPO can be substantial, often ranging between 7% and 10% of the funds raised.
Higher Cost of Capital
Post-IPO, companies may face an increased cost of capital due to market perceptions and regulatory requirements.
Key Considerations for Investors
Strong Management

Investors seek companies with a proven leadership team and experience in public company operations.
Robust Growth
Consistent revenue growth and a large addressable market are crucial. Companies should demonstrate solid revenue performance over several years.
Path to Profitability
A clear and credible path to profitability is essential, especially for venture-backed firms that may prioritise growth over immediate profits.
Defensible Competitive Advantage
A unique market position or competitive edge that protects against rivals is vital for attracting investor interest.
Appropriate Valuation
The company’s valuation should align with public market comparables, reflecting growth expectations and industry standards.
Effective Use of Proceeds
A well-defined plan for utilising IPO funds to drive business growth is crucial for investor confidence.
The IPO Process: Step-by-Step
1. Assemble the Right IPO Team

Successful IPOs require a team of experts, including:
- Investment Bank: Underwrites the offering, conducts valuation analysis, facilitates roadshows, and stabilises aftermarket trading.
- Legal Counsel: Advises on regulatory compliance, disclosure responsibilities, and risk assessments.
- Auditor: Ensures financial records are accurate and complete.
- Financial PR/IR: Manages investor relations and media communications.
- Industry Experts: Provides insight into market trends and competitive dynamics.
2. Pre-IPO Preparations
Before going public, companies must:
- Update Financial Records: Align financial statements with public company standards.
- Develop Business Plans: Create multi-year plans outlining growth strategies and competitive positioning.
- Conduct IP Audit: Review and optimise intellectual property protections.
- Revise Bylaws: Update governance provisions to meet public market requirements.
- Hire Key Personnel: Recruit staff with public company experience.
3. Declare Intention and File Registration
Submit an S-1 registration statement or equivalent to securities regulators, including:
- Business Overview: Company history, products/services, and value proposition.
- Market Opportunity: Assessment of growth potential and market conditions.
- Competition: Analysis of competitive landscape and barriers to entry.
- Risk Factors: Discussion of potential risks and impacts on financials.
- Use of Proceeds: Detailed plan for fund allocation.
- Management Team: Backgrounds of key executives and board members.
- Financial Statements: Two years of audited financials and the latest stub period.
- Capitalisation Table: Breakdown of current equity ownership.
4. Investor Roadshow

Conduct a roadshow to pitch the IPO to institutional investors:
- Presentation: Detailed slide deck covering growth opportunities and financial forecasts.
- One-on-One Meetings: Private sessions for in-depth due diligence.
- Feedback and Orders: Adjust pricing and allocation based on investor interest.
5. Pricing and Distribution
- Final Pricing: Set IPO price based on demand and market conditions.
- Share Allocation: Distribute shares to investors based on order size and strategy.
- Lock-Up Agreements: Restrict insiders from selling shares for 180 days to prevent market disruption.
6. Execution and Aftermarket Support
- Greenshoe Option: Allow underwriters to repurchase shares to stabilise trading.
- Price Stabilization: Implement strategies to support the share price.
- Liquidity Provisioning: Maintain active trading to ensure market stability.
Structuring the SME IPO Deal

Offer Size
Balance the number of primary and secondary shares to meet capital needs while minimising dilution. Typical IPO sizes range from $10 million to $100 million.
Share Class Structure
Determine whether to offer common shares or a dual-class structure, which allows insiders to retain voting control.
Price Range
Set a preliminary price range during roadshows but finalise based on demand and market feedback.
Use of Proceeds
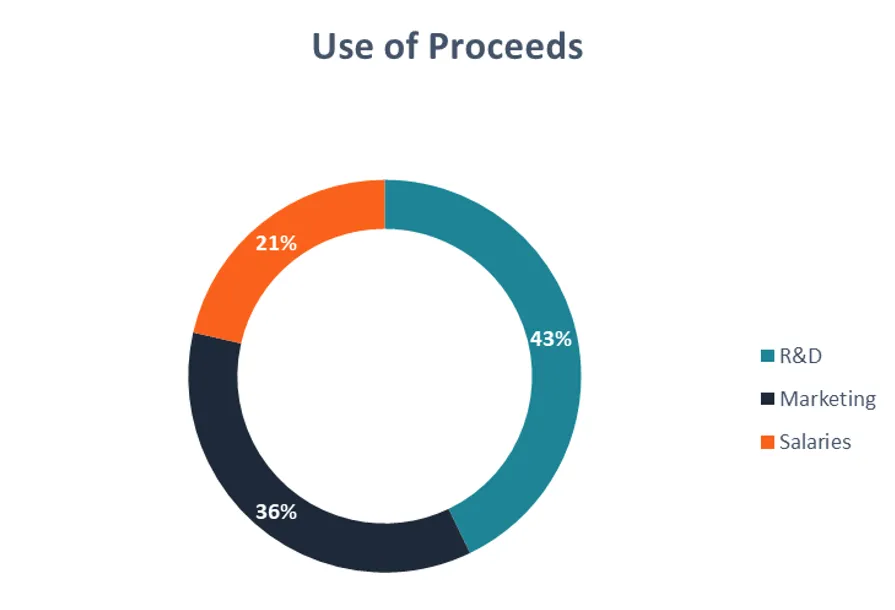
Clearly articulate how IPO funds will support growth and strategic initiatives.
Lock-Up Agreements
Implement a six-month lock-up period for insiders to prevent market instability.
Greenshoe Provision
Consider a greenshoe option to manage trading volatility and support stock performance.
Institutional vs Retail Allocation

Allocate shares to institutional investors to ensure a successful offering, with a possible portion reserved for retail investors.
Conclusion
An SME IPO represents a transformative opportunity for growth and expansion. By understanding the complexities and carefully navigating the process, SMEs can leverage the public markets to achieve their strategic goals. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for aspiring entrepreneurs, ensuring they are well-prepared to embark on this exciting journey.