Understanding your idea’s potential viability is essential before starting a new business venture. Conducting a feasibility analysis is a critical step that enables businesses to assess the potential for success or failure. This analysis dives into a new project’s practical and financial implications, providing a clear view of what’s needed to succeed in a competitive market. This guide will walk through the primary elements of feasibility analysis, helping you gain insights into making informed business decisions.
What is a Feasibility Analysis?

A feasibility analysis examines the viability of a business idea, assessing whether the proposed project is likely to be successful. It considers factors such as market demand, resources, and risks. By performing this analysis, businesses can identify potential roadblocks, determine if the idea aligns with their goals, and estimate the return on investment. This process saves time and resources and builds a foundation for strategic planning.
Critical Components of a Feasibility Analysis
Breaking down the feasibility study into specific, structured areas allows for a thorough assessment. The main components include:
- Market Feasibility
- Technical Feasibility
- Financial Feasibility
- Organisational Feasibility
- Legal and Regulatory Feasibility
Let’s explore each of these in detail.
1. Market Feasibility: Assessing Demand and Competition
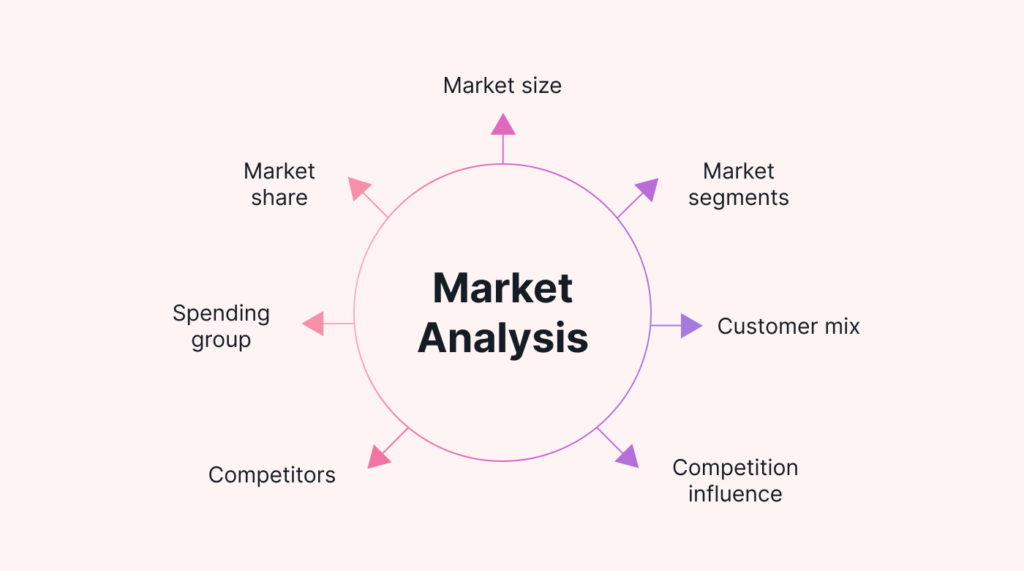
Market feasibility is one of the most crucial aspects of the feasibility analysis. It determines if there’s a demand for your product or service and identifies your target audience. An in-depth market analysis should include:
- Target Audience Identification: Who are the customers most likely to purchase your product? What are their demographics, preferences, and buying habits?
- Market Demand Analysis: How large is the potential market? Are there trends showing growing demand for similar products?
- Competitive Landscape: Who are the main competitors? What is their pricing strategy, and what advantages do they offer?
2. Technical Feasibility: Analyzing Operational Requirements
Technical feasibility assesses the practicality of the technology, production processes, and skills required to develop and deliver the product or service. This involves:
- Resource Requirements: What resources are needed, including tools, facilities, and workforce?
- Operational Processes: Is there a clear production or operational plan? Consider each stage from procurement to delivery.
- Skill Requirements: Do you have access to a team with the necessary skills? If not, what training or hiring will be required?
3. Financial Feasibility: Budgeting and Profitability Projections

Financial feasibility examines the economic aspects of the project, focusing on cost estimates, revenue potential, and profitability. Critical steps in this process include:
- Cost Analysis: Break down all initial and ongoing expenses, including equipment, staff, materials, marketing, and overheads.
- Revenue Projections: Estimate potential revenue based on pricing, sales volume, and market share. Consider different scenarios, from conservative to optimistic.
- Breakeven Analysis: Calculate how your business will begin to generate profit. This analysis shows how long it will take to recover initial investments.
- Funding Needs and Sources: Determine if additional funding is required. Explore different financing options like loans, grants, or investor backing.
4. Organizational Feasibility: Assessing Internal Capacity
Organisational feasibility assesses whether your business has the management expertise, skills, and structure to complete the project. This involves:
- Management Capability: Does the management team have the experience and knowledge to drive the business toward success?
- Operational Structure: Do you have the proper organisational setup, including departments and roles?
- Human Resource Requirements: Will your business need to hire additional staff? If so, what skills and experience will they need?
5. Legal and Regulatory Feasibility: Compliance and Risk Assessment

Every business must comply with legal and regulatory standards specific to its industry and location. Assessing this includes:
- Licenses and Permits: Identify any necessary licenses, permits, or approvals.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensure your operations meet industry regulations, including health, safety, and quality standards.
- Risk Assessment: Analyze potential legal risks, including intellectual property issues, environmental considerations, and insurance needs.
Steps to Conduct a Feasibility Analysis
The feasibility analysis is a structured process that involves various steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Conduct Preliminary Analysis
A preliminary analysis is a quick assessment of whether it’s worth conducting a complete feasibility study. In this phase, brainstorm possible challenges and briefly evaluate market demand, competitive presence, and resource availability.
Step 2: Outline the Project Scope and Objectives
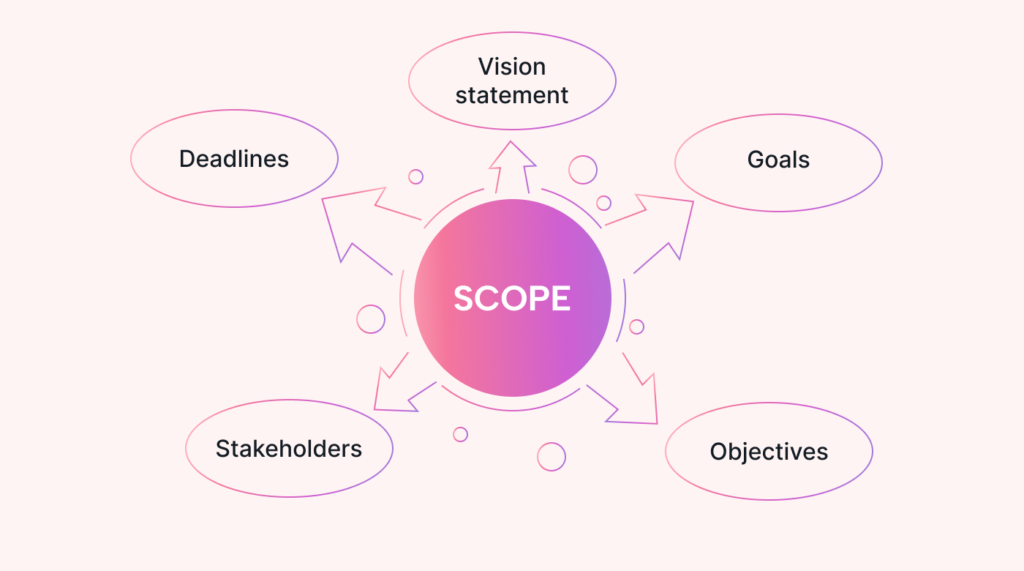
Define your project’s scope and set clear objectives. Outline the project’s requirements, identify specific goals, and establish the time frame. A well-defined scope will help maintain focus and ensure all aspects of the feasibility analysis align with the business’s objectives.
Step 3: Perform a Market Survey and Research
Conduct a comprehensive market survey to understand your audience, market trends, and competition. Collect data through surveys, interviews, and online research. Identify any market gaps and analyse customer needs.
Step 4: Develop Financial Projections

Financial projections are central to the feasibility analysis, offering insights into profitability and cost management. To gauge realistic financial viability, use conservative estimates for revenue and expenses. Prepare income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow projections.
Step 5: Analyze Operational Requirements and Resources
Determine all operational requirements, including technology, production processes, and staffing. Assess the capacity of your current resources and identify any additional resources needed. Create a detailed list of required assets and estimate associated costs.
Step 6: Assess Risks and Potential Challenges

Identify potential risks and challenges your project might face, such as economic downturns, market shifts, or regulatory changes. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks, including contingency plans for financial and operational challenges.
Step 7: Review and Make Decisions
Compile the data from each feasibility study phase and analyse the findings. Then, make informed decisions about whether to proceed with your business idea, adjust it, or reconsider it.
Benefits of Conducting a Feasibility Analysis
Conducting a feasibility analysis is more than just a precaution; it offers substantial benefits that enhance your business’s potential for success:
- Risk Reduction: A feasibility analysis reduces the risk of costly setbacks by identifying and addressing potential issues early.
- Clear Business Direction: This process clarifies strategic goals, allowing businesses to approach new projects with a strong direction.
- Resource Allocation Efficiency: A detailed analysis can help allocate resources more effectively, optimising time and capital.
- Increased Investor Confidence: A thorough feasibility study builds credibility, making securing funding from investors and stakeholders easier.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Feasibility Analysis

Avoid these common pitfalls to ensure a comprehensive and practical feasibility analysis:
- Overestimating Market Demand: Ensure your market research is realistic and backed by reliable data to avoid inflated projections.
- Ignoring Financial Details: Every cost factor must be considered; failing to account for all expenses can lead to financial shortfalls.
- Underestimating Competition: Thoroughly analyse competitors to understand what sets your business apart and how to capture market share.
- Rushing the Process: A feasibility analysis requires time and careful consideration. Rushing through it can lead to overlooked risks and missed opportunities.
Conclusion: The Role of Feasibility Analysis in Business Success
A feasibility analysis is not just a formality; it’s an essential tool for identifying the viability of a business idea. Businesses can assess market demand, financial feasibility, operational requirements, and organisational capabilities by conducting a thorough analysis. The outcome of this analysis is invaluable, offering a roadmap to move forward with confidence or adjust plans as needed.
Conducting a feasibility study is a proactive step toward sustainable growth. It helps businesses avoid potential pitfalls and make well-informed decisions. By understanding every aspect of feasibility—market, technical, financial, organisational, and legal—you equip your business with the insights needed to pursue new opportunities and achieve long-term success.












