Raising capital is crucial for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to fuel their growth and expansion. While large corporations have numerous avenues for capital, SMEs often face unique challenges, including limited investor bases and stringent documentation requirements. This guide delves into the SME IPO (Initial Public Offering) process, outlining each step comprehensively to help SMEs navigate the complexities and achieve successful listings on BSE SME and NSE Emerge stock exchanges.
Understanding SME IPOs: An Overview

An SME IPO provides an alternative route for small and medium enterprises to raise capital by listing their shares on stock exchanges. This process enables SMEs to secure necessary funds and offers investors a chance to invest in high-growth potential companies at relatively lower costs. The dual benefits of capital infusion for SMEs and attractive investment opportunities for investors make SME IPOs a win-win scenario.
Step-by-Step Guide to the SME IPO Listing Process
1. IPO Planning and Preparation

Assemble Your IPO Team
Form a dedicated IPO team comprising company promoters, managers, and external advisors. This team will oversee the IPO process and ensure that all aspects are handled efficiently.
Engage an Investment Bank
Hire an experienced investment bank to guide you through the IPO journey. Their expertise is crucial for navigating regulatory requirements and market conditions.
Evaluate Your Eligibility
Assess your company’s readiness for an SME IPO. Before proceeding, evaluate the current valuation, capital needs, and other prerequisites.
2. Eligibility Criteria for SME IPO

Meet Listing Requirements
Ensure your company meets the necessary criteria, including profitability, minimum paid-up capital, and a solid operational track record.
Company Registration
Confirm that your company is registered under the Companies Act 1956/2013. For partnerships or LLPs, the net worth should be at least Rs. 1 crore for the past two financial years.
Gather Essential Documents
Prepare crucial documents such as meeting minutes, articles of association, and internal approvals from shareholders and the board.
3. Due Diligence and Merchant Banker Appointment

Hire a SEBI-Registered Merchant Banker
Engage a SEBI-registered merchant banker to handle the IPO process. They will prepare the IPO offer documents, file the prospectus, and determine the issue price.
Conduct Due Diligence
The merchant banker will perform thorough due diligence to verify document accuracy, underwriting services, and investor attraction strategies.
4. Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) Submission

Prepare and File DRHP
The merchant banker drafts the DRHP, which includes vital company information, financial performance, and risk factors. Then, the DRHP is submitted to the stock exchange for review.
Ensure Accuracy
Since the DRHP is a crucial document for investor decisions, ensure it is comprehensive and accessible to discrepancies.
5. In-principle approval for DRHP

Stock Exchange Review
The stock exchange reviews the DRHP, conducts site visits, and performs investigations through the Listing Advisory Committee.
Obtain Approval or Address Discrepancies
Based on the review, the exchange either grants in-principal approval or highlights necessary corrections.
6. File Prospectus with Registrar of Companies (RoC)

Submit Red Herring Prospectus (RHP)
Post-approval, submit the RHP to the RoC. This document details the issue price, IPO timetable, and other critical information.
Determine IPO Issue Price
The merchant banker evaluates company valuation to set the IPO issue price, essential for determining lot sizes.
Publicise the Prospectus
Publish the DRHP and RHP on the merchant banker’s website and advertise the IPO through roadshows and investor meetings.
7. IPO Launch

Initiate IPO Subscription
The IPO is launched on a pre-set date, allowing investors to subscribe. They can invest in shares with a minimum lot size until closing.
Subscription Details
Investors can buy shares in multiples of Rs. 1,00,000 or more, depending on the lot size.
8. Allotment of IPO Shares
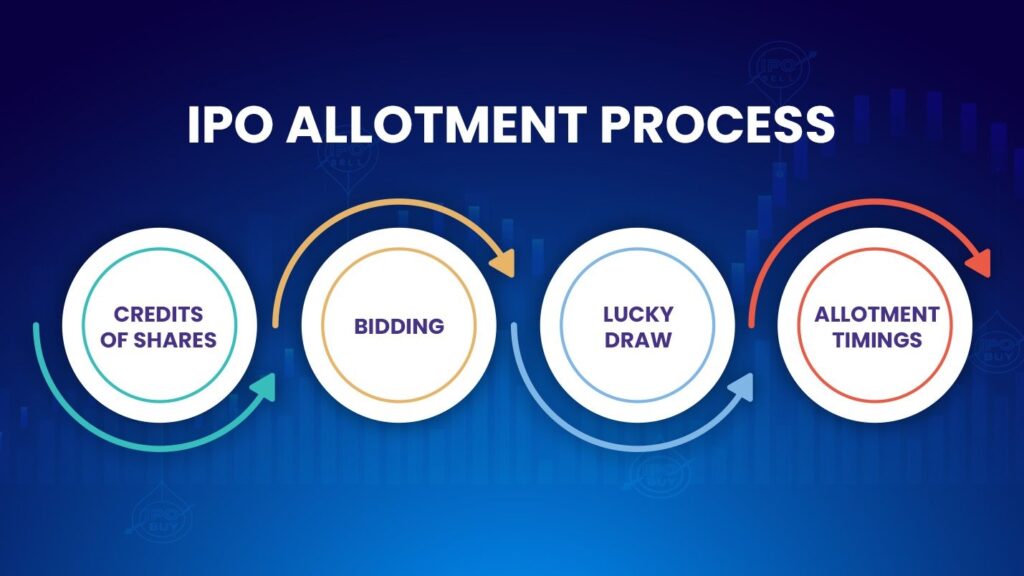
Process Applications
The Register and Transfer Agent (RTA) processes IPO applications and allocates shares to investors based on categories such as retail and non-retail.
Publish Basis of Allotment (BoA)
The registrar publishes the BoA in a prominent newspaper, detailing application volumes, share allocations, and subscription rates.
9. Listing of SME IPO

Stock Exchange Listing
The SME is officially listed on the stock exchange with a unique symbol, ISIN, and security code. Trading commences on the listing day.
Trading Regulations
Shares can only be traded in lots, not individually.
Conclusion: The Strategic Advantage of SME IPOs
An SME IPO offers small and medium enterprises a valuable opportunity to raise capital, bypassing traditional investor constraints. With regulatory relaxations and streamlined processes, SMEs can leverage this route to enhance their growth prospects and contribute significantly to the national economy. Understanding and mastering the IPO process becomes essential for unlocking its full potential as the SME sector evolves.